Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 591, p.154914_1 - 154914_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0The amount of corrosion of austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC was evaluated considering the changes in solution composition and boiling during actual concentration operations. Austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC is the structural material of the highly radioactive liquid waste concentrator in Japanese spent fuel reprocessing plant, which treats highly corrosive nitric acid solutions during enrichment operations. The study results show that it is necessary to focus on nitric acid concentrations, oxidizing metal ion concentrations, and decompression boiling as factors that accelerate the corrosion rate of stainless steel because of cathodic reaction activation.
Miura, Takatomo; Kudo, Atsunari; Koyama, Daisuke; Obu, Tomoyuki; Samoto, Hirotaka
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) had reprocessed 1,140 tons of spent fuel discharged from commercial reactors (BWR, PWR) and Advanced Thermal Reactor "Fugen" from 1977 to 2007. TRP had entered decommissioning stage in 2018. In order to reduce the risk of High Active Liquid Waste (HALW) held at the facility, the vitrification of HALW is given top priority. HALW generated from reprocessing of spent fuel contains not only fission products (FPs) but also trace amounts of uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu) within the liquid and insoluble residues (sludge). Under normal conditions, concentrations of U and Pu in HALW are very low so that it can not reach criticality. Since FPs with high neutron absorption effect coexists in HALW, even if the cooling function is lost due to serious accident and HALW evaporates to dryness, it is considered that criticality would not been reached. In order to confirm this estimation quantitatively, criticality safety evaluations were carried out for the increase of U and Pu concentrations by evaporation of HALW to the point of dryness. In this evaluation, infinite multiplication factors were calculated for each of solution system and sludge system of HALW with respect to the concentration change through evaporation to dryness. It is confirmed it could not reach criticality. The abundance ratios of U, Pu and FPs were set conservatively based on analytical data and ORIGEN calculation results. Multiplation factors for two-layer infinite slab model of solution and sludge systems of HALW were also calculated, and it was confirmed it could not reached criticality. In conclusion, the result was gaind that there could be no criticality even in the process through evaporation to dryness of HALW in TRP.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2023-001, 26 Pages, 2023/05
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into the atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an analytical approach has been developed using computer simulation programs to assess the radioactive source term from those facilities. The proposed approach consists analyses with three computer programs. At first, the simulation of boiling behavior in the HLLW tank is conducted with SHAWED code. Next step, the thermal-hydraulic behavior in the facility building is simulated with MELCOR code based on the results at the first step simulation such as flowed out mixed steam flow rate, temperature and volatilized Ru from the tank. The final analysis step is carried out for estimating amount of released radioactive materials with SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitric acid, nitrogen oxide and Ru based on the condition also simulated MELCOR. Series of sample simulations of the accident at a hypothetical typical facility are presented with the data transfer between those codes in this report.
Togawa, Orihiko; Okura, Takehisa; Kimura, Masanori
JAEA-Review 2022-049, 76 Pages, 2023/01
Before construction and after operation of nuclear facilities, environmental consequence assessments are conducted for normal operation and an emergency. These assessments mainly aim at confirming safety for the public around the facilities and producing relief for them. Environmental consequence assessments are carried out using observations/ measurements by environmental monitoring and/or model predictions by calculation models, sometimes using either of which and at other times using both them, according to the situations and necessities. First, this report investigates methods, roles, merits/demerits and relationship between observations/measurements and model predictions which are used for environmental consequence assessments of nuclear facilities, especially holding up a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at Rokkasho, Aomori as an example. Next, it explains representative examples of utilization of data on observations/measurements and results on model predictions, and considers points of attention at using them. Finally, the report describes future direction, for example, improvements of observations/measurements and model predictions, and fusion of both them.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2022-011, 37 Pages, 2022/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. Two major mechanisms are expected for fission products (FPs) transfer from liquid to vapor phase. One is non-volatiles FPs transfer in the form of mists to the vapor phase in the tank, the other is volatilization of such as Ruthenium. These FPs transferred to the vapor phase in the tank could be released with water and nitric-acid mixed steam and NO gas flow to the environment. NO
gas flow to the environment. NO is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (
is generated from denitration of nitrate fission products during dry out phase. These phenomena occurred in this accident originate from the liquid waste boiling in the tank. It is essential for the risk assessment of this accident to simulate thermo-hydraulic and chemical behaviors in the waste tank quantitatively with a versatile computer program. The SHAWED (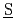 imulation of
imulation of 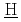 igh-level radio
igh-level radio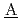 ctive
ctive 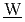 aste
aste 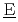 vaporation and
vaporation and 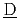 ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
ryness) has been developed to realize these requirements. In this report, detailed description of major analytical models is explained based on the features of this accident, and some simulation examples are also described for the use in an actual risk assessment.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-013, 20 Pages, 2022/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. An idea has been proposed to implement a steam condenser as an accident countermeasure. This measure is expected to prevent nitric acid steam diffusing in facility building and to increase gaseous Ru trapping ratio into condensed water. A simulation study has been carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building to analyze the efficiency of steam condenser. In this study, SCHERN computer code simulates chemical behaviors of Ru in nitrogen oxide, nitric acid and water mixed vapor based on the conditions obtained from simulation with thermal-hydraulic computer code MELCOR. The effectiveness of steam condenser has been analyzed quantitively in preventing mixed vapor diffusion and gaseous Ru trapping effect. Some issues to be solved in analytical model has been also clarified in this study.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Research 2021-005, 25 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. Accurate quantitative estimation of released Ru is one of the important issues for risk assessment of those facilities. To resolve this issue, an empirical correlation equation of Ru mass transfer coefficient across the vapor-liquid surface, which can be useful for quantitative simulation of Ru mitigating behavior, has been obtained from data analyses of small-scale experiments conducted to clarify gaseous Ru migrating behavior under steam-condensing condition. A simulation study has been also carried out with a hypothetical typical facility building successfully to demonstrate the feasibility of quantitative estimation of amount of Ru migrating in the facility using the obtained correlation equation implemented in SCHERN computer code which simulates chemical behaviors of nitrogen oxide based on the condition also simulated thermal-hydraulic computer code.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Hiyama, Mina*
JAEA-Data/Code 2021-008, 35 Pages, 2021/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NO ) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO
) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects to the migration behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NO with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. The analysis program, SCHERN has been under developed to simulate chemical behavior including Ru coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building. This technical guide for SCHERN-V2 presents the overview of covered accident, analytical models including newly developed models, differential equations for numerical solution, and user instructions.
Maruyama, Yu; Yoshida, Kazuo
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 63(7), p.517 - 522, 2021/07
, 63(7), p.517 - 522, 2021/07
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Masanao
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 56(1), p.17 - 25, 2021/03
The Tokai Reprocessing Plant is the first reprocessing plant in Japan which started hot test in 1977, and had reprocessed 1140 tons of spent nuclear fuel by May 2007. The gaseous and liquid radioactive wastes has been discharged to the environment. Since iodine-129 ( I) is one of the most important nuclides for environmental impact assessment. Therefore,
I) is one of the most important nuclides for environmental impact assessment. Therefore,  I in the exhaust and effluent has been controlled, and a precise analysis method of
I in the exhaust and effluent has been controlled, and a precise analysis method of  I in the environmental samples was developed, and the concentration of 129I in the environment was investigated. This report presents an overview of these activities. Not limited to
I in the environmental samples was developed, and the concentration of 129I in the environment was investigated. This report presents an overview of these activities. Not limited to  I on reprocessing facilities, it is essential for nuclear operators to reduce the amount released to the environment in the spirit of ALARA, and to continuously develop the further upgrading environmental monitoring methods and evaluation methods in order to foster a sense of safety and security among residents living in the vicinity of the facilities.
I on reprocessing facilities, it is essential for nuclear operators to reduce the amount released to the environment in the spirit of ALARA, and to continuously develop the further upgrading environmental monitoring methods and evaluation methods in order to foster a sense of safety and security among residents living in the vicinity of the facilities.
Miwa, Kazuji; Obata, Hajime*; Suzuki, Takashi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(5), p.537 - 545, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the vertical distribution of Iodine-129 ( I) which is mainly produced by European nuclear reprocessing plants in the Chukchi Sea and Bering Sea.
I) which is mainly produced by European nuclear reprocessing plants in the Chukchi Sea and Bering Sea.  I was found to be distributed almost uniformly in fallout level, and an increasing in
I was found to be distributed almost uniformly in fallout level, and an increasing in  I concentration levels caused by high
I concentration levels caused by high  I water inflow from the Atlantic Ocean was not observed. Additionally, we revealed the vertical distribution of iodide, one chemical form of iodine, from the Bering Shelf area to the Chukchi Sea for the first time. The increasing tendency of iodide near sea bottom was observed.
I water inflow from the Atlantic Ocean was not observed. Additionally, we revealed the vertical distribution of iodide, one chemical form of iodine, from the Bering Shelf area to the Chukchi Sea for the first time. The increasing tendency of iodide near sea bottom was observed.
Hiyama, Mina*; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Data/Code 2019-006, 17 Pages, 2019/07
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides (NOx) are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that NOx affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru at the anticipated atmosphere condition in cells and/or compartments of the facility building. Chemical reactions of NOx with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis program has been developed to simulate chemical reaction coupled with the thermo-hydraulic condition in the flow paths in the facility building.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 18(2), p.69 - 80, 2019/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, volatile radioactive materials, such as ruthenium (Ru) are released from the tanks with water and nitric-acid mixed vapor into atmosphere. In addition to this, nitrogen oxides are also released formed by the thermal decomposition of metal nitrates of fission products (FP) in HLLW. It has been observed experimentally that nitrogen oxide affects strongly to the transport behavior of Ru. Chemical reactions of nitrogen oxide with water and nitric acid are also recognized as the complex phenomena to undergo simultaneously in the vapor and liquid phases. An analysis method has been developed with coupling two types of computer codes to simulate not only thermo-hydraulic behavior but also chemical reactions in the flow paths of carrier gases. A simulation study has been also carried out with a typical facility building.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Naoki; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
JAEA-Research 2017-015, 18 Pages, 2018/01
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste is postulated as one of the severe accidents at a fuel reprocessing facility. It was observed at the experiments that a large amount of ruthenium (Ru) is volatilized and transfer to the vapor phase in the tank. The nitric acid and water mixed vapor released from the tank is condensed. Volatilized Ru is expected to transfer into the condensed water at the compartments in the building. Quantitative estimation of the amount of Ru transferred condensed water is key issues to evaluate the reduction the amount of Ru through leak path in the facility building. This report presents that a correlation has been developed for Ru transfer rate to condensed water with vapor condensing rate based on the experimental results and additional thermal-hydraulic simulation of the experiments. Applicability of the correlation has been also demonstrated with the accident simulation of typical facilities in full-scale.
 -radiolysis of nitric acid solution
-radiolysis of nitric acid solutionIshijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(2), p.100 - 106, 2017/05
Zirconium (Zr) has been used as a structural material at the spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Japan because of its excellent corrosion resistance against nitric acid solution. And the radiolytic hydrogen is known to be generated in the spent nuclear fuel solution. Zr is known to be highly susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. Therefore, evaluating the radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior of Zr in nitric acid solution (HNO ) is essential. In this study, immersion tests were conducted on Zr in nitric acid solutions under
) is essential. In this study, immersion tests were conducted on Zr in nitric acid solutions under  -ray irradiation to evaluate its radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior. Results showed that hydrogen concentration on Zr increased both in 1-3 mol/L HNO
-ray irradiation to evaluate its radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior. Results showed that hydrogen concentration on Zr increased both in 1-3 mol/L HNO and pure water at 5 and 7 kGy/h after immersion. The amount of hydrogen absorption on Zr under
and pure water at 5 and 7 kGy/h after immersion. The amount of hydrogen absorption on Zr under  -ray irradiation had a direct correlation with the radiolytic hydrogen generation value in HNO
-ray irradiation had a direct correlation with the radiolytic hydrogen generation value in HNO . The results of glow discharge optical emission spectrometry, thermal desorption spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction result shows that the absorbed radiolytic hydrogen generated a hydride on the surface of Zr.
. The results of glow discharge optical emission spectrometry, thermal desorption spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction result shows that the absorbed radiolytic hydrogen generated a hydride on the surface of Zr.
Matsueda, Makoto; Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki; Matsui, Hiroki
Proceedings of 54th Annual Meeting of Hot Laboratories and Remote Handling (HOTLAB 2017) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2017/00
In the PUREX method, spent fuels are dissolved with nitric acid media. The reprocessing solution containing Fission Products derived from spent fuels is very corrosive to metal materials, the corrosion problem often appears on the surface stainless steel devices. The oxidizing metal ions such as Ruthenium (Ru) and Neptunium (Np) in the process solution is the key reason for severe corrosion of stainless steel. In order to obtain the corrosion rate of stainless steel, we installed the corrosion test apparatus inside an airtight concrete cell in a hot laboratory (the WAste Safety TEsting Facility (WASTEF) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency), and performed the corrosion tests of stainless steel in the heated nitric acid solution containing Np. The corrosion tests were performed in the temperature range from room temperature to boiling point for 500 hours per batch. The results show that the presence of Np accelerate the stainless steel corrosion in the nitric acid solution.
Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Research 2016-012, 24 Pages, 2016/08
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste is postulated as one of the severe accidents. In this case, Ru volatilization increases in liquid waste temperature over 120 centigrade at later boiling and dry out phases. It has been observed at the experiments with actual and synthetic liquid waste that some amount of Ru volatilizes and transfers into condensed nitric acid solution at those phases. The nitric acid and water vapor from waste tank condenses at compartments of actual facilities building. The volatilized Ru could transfer into condensed liquid. It is key issues for quantifying the amount of transferred Ru through the facility building to simulate these thermodynamic and chemical behaviors. An analytical model has been proposed in this report based on the condensation mechanisms of nitric acid and water in vapor-liquid equilibria. It has been also carried out to review the thermodynamic properties of nitric acid solution.
Yoshida, Kazuo
JAEA-Research 2016-004, 15 Pages, 2016/06
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste is postulated as one of the severe accidents caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, some amount of fission products (FPs) will be transferred to the vapor phase in the tank, and could be released to the environment. Two mitigative accident measures have been proposed by the licensee. One of them is injecting cold water to waste tanks to prevent dryness and another is leading generated vapor through temporary duct to huge spaces in the facility to condense to liquid. Thermal-hydraulics and aerosol transport behaviors in compartments of a typical facility building have been analyzed based on the scenario with these accident measures. The effects of measures are discussed form a view point of the reduction of radioactive material release to environment.
Yoshida, Kazuo; Ishikawa, Jun; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 14(4), p.213 - 226, 2015/12
An accident of evaporation to dryness by boiling of high level liquid waste (HLLW) is postulated as one of the severe accidents to occur caused by the loss of cooling function at a fuel reprocessing plant. In this case, some amount of fission products (FPs) will be transferred to the vapor phase in the tank, and could be released to the environment. Therefore, the quantitative estimation of transport and release behavior of FPs is one of the key issues in the assessment of the accident consequence. To resolve this issue, a systematic analysis method with computer codes has been developed based on the phenomenological behavior in boiling accident of HLLW. A simulation study demonstrated that the behaviors of liquid waste temperature and entrainment of mists were in good agreement with the experimental results during early boiling phase
Kinuhata, Hiroshi*; Yamamoto, Masahiko; Taguchi, Shigeo; Surugaya, Naoki; Sato, Soichi; Kodama, Takashi*; Tamauchi, Yoshikazu*; Shibata, Yuki*; Anzai, Kiyoshi*; Matsuoka, Shingo*
Nuclear Technology, 192(2), p.155 - 159, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Experiments using a small-scale apparatus with 30 ml actual high-level liquid waste from the Tokai Reprocessing Plant were carried out to show that the hydrogen concentration in the gas phase reaches a steady-state value of much less than 4% (lower explosive limit) in the absence of sweeping-air. The H concentration reached a steady-state value as was expected and it was compared with a value predicted from an equation with parameters which had been obtained using the simulated solution. Satisfactory agreement showed that the Pd-ion catalytic H
concentration reached a steady-state value as was expected and it was compared with a value predicted from an equation with parameters which had been obtained using the simulated solution. Satisfactory agreement showed that the Pd-ion catalytic H consumption reaction previously found in the simulated solution proceeded equally well in the actual solution.
consumption reaction previously found in the simulated solution proceeded equally well in the actual solution.